The process of how solar power works isn’t all that complicated. Today we’re going to share the ins and outs of how solar power works to help you understand the physics behind solar power. With renewable energy, wind, and solar among the top, being the future of energy as a whole it’s important you know how the process works!
The current is moved around from the solar panel to the power box and returned out as power to your home for use. Okay, so that’s a little simpler than it really is. Let’s walk the process back to the beginning of the steps.
Solar cells soak up the sunshine. When the sunlight rays, known as photons hit the electron it causes the electron to bounce off the solar panels. The current from this process is then transferred to an inverter box that will make the DC go to AC which is what our homes use for energy.
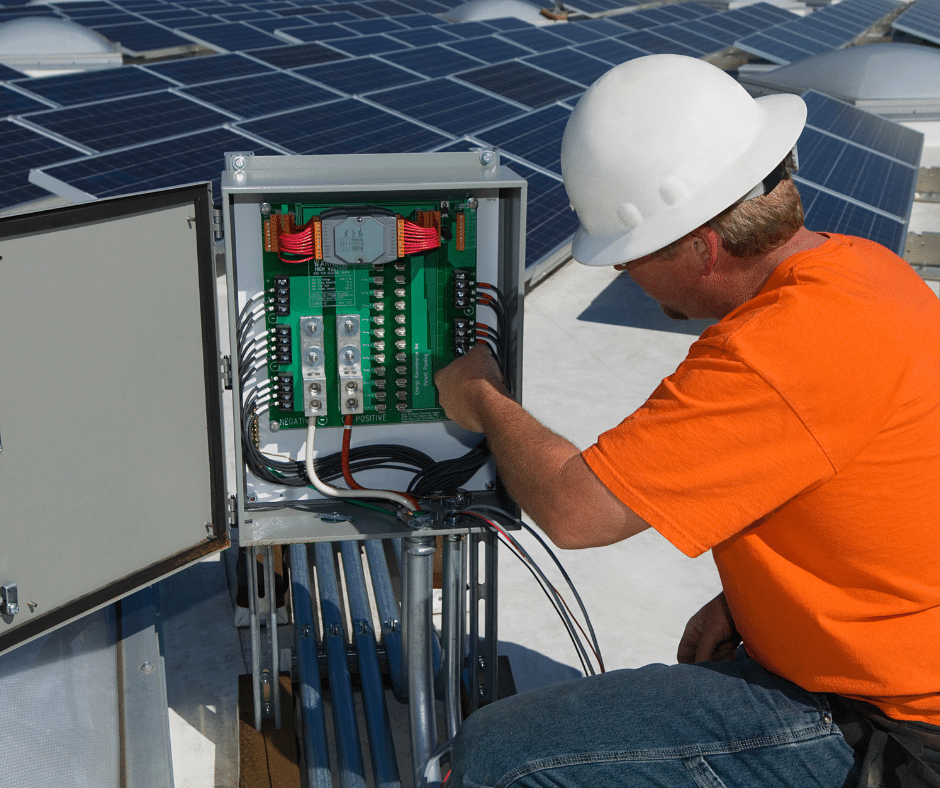
The reason DC is converted to AC is that that’s what our electric grid is running on. The DC needs to be converted to whatever type of energy the main grid uses so that the power grid can then return the proper current back out for use in homes.
In time you’ll start to see more homes using solar panels as it’s the most cost-effective option for most homeowners in the world. Having a few solar panels on the roof of the home is somewhat simple to do and while the beginning part of using solar panels is a larger investment, over time you gain the money back in revenue from the electricity you produce and don’t use.
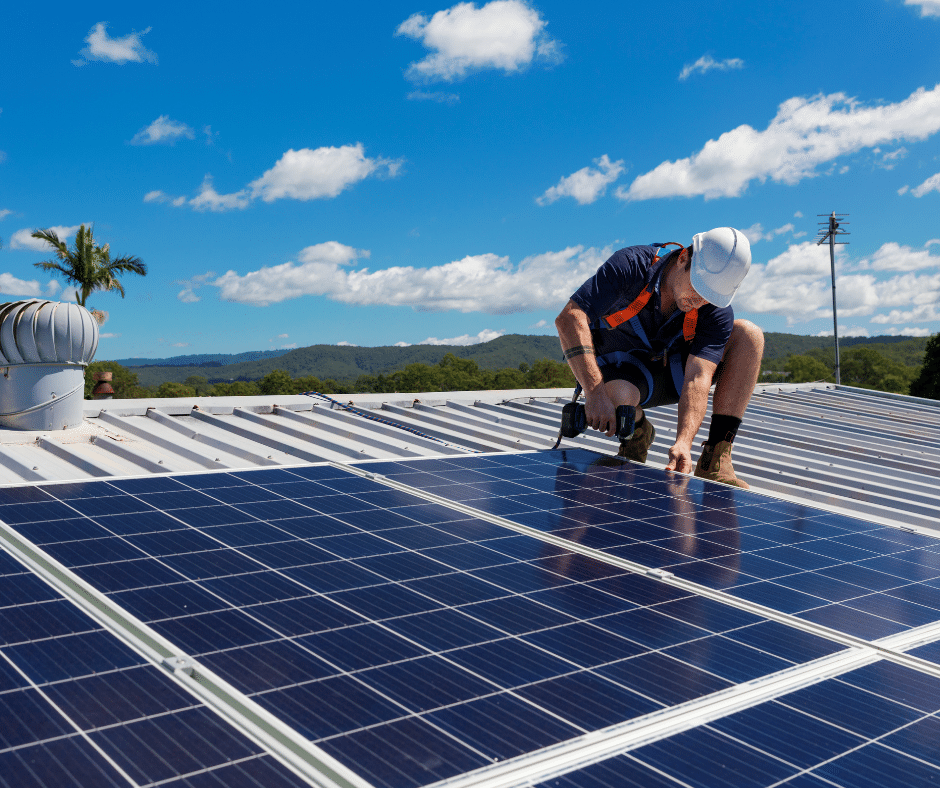
The electricity that your solar panels produce but don’t use, is sold off back into the grid and appears as a credit on your electric bill, or in some cases, a check in the mail.
Whether you use solar panels for heat, electricity, or heating water doesn’t matter. The starting process of the physics behind solar power is all the same. You’re converting a photon into an electron then from a DC type of electricity to an AC electricity to fuel your home’s needs!
